There are several reasons why women are more prone to bone loss and osteoporosis, which is why our team here at Camelback Spine Care is dedicated to osteoporosis prevention
A LOOK AT BONE DEVELOPMENT
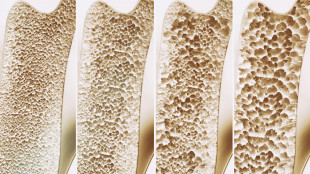
The differences in bone structure between men and women begin during development. Peak bone mass in women occurs at the age of 18, while men reach peak bone mass at the age of 20. In general, the initial development of bones is less in women than men and women typically have thinner bones with less bone mass.Once peak bone mass is achieved in either gender, bone strength depends on the resorption and formation rate of the bone tissue. Under ideal circumstances, these rates are neutral and don't affect bone density, as bone reformation keeps pace with bone loss.When the formation rate of bone tissue falls behind the resorption rate, bone density loss occurs. This imbalance tends to increase with age in both men and women, to be sure but men don't undergo the same abrupt hormonal changes as women later in life.
OSTEOPOROSIS AND MENOPAUSE
The passage through menopause, with its subsequent and significant drop in the sex hormones (namely estrogen), greatly affects bone density. In fact, the period following the transition through menopause is when many women lose the most bone mass.Men, on the other hand, only experience a gradual decline in their sex hormone (testosterone) levels as they grow older.
OSTEOPOROSIS AND YOUR SPINE
Bone loss and osteoporosis can affect all of the bones in your body, but as spine specialists, we want to focus on this area. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that the prevalence of osteoporosis in the cervical (neck) and lumbar (lower back) regions of the spine in people over the age of 50 is higher among women at 19.6% versus only 4.4% for men. Bone loss in your spine can lead to painful conditions like compression fractures and leave you more vulnerable to arthritis.
COMBATING OSTEOPOROSIS
At our practice, we offer several preventive measures for women who are facing bone loss, including:
Estrogen replacement therapy
Selective estrogen receptor modulators
Calcitonin nasal spray
Bisphosphonates
In addition to these treatments, we also recommend lifestyle changes, such as exercising more and quitting smoking, which greatly interferes with your body and it's ability to remodel bone.If your osteoporosis does lead to a fracture in your spine, we can turn to a vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty to stabilize the bone and restore height to your vertebra. The key to treating osteoporosis is to take action before a fracture occurs, which is why we encourage you to come see us for an evaluation. To get started, contact one of our two offices in Sun City or Phoenix, Arizona.
.jpg)


.jpg)